Educational Objectives
BS IE PROGRAM SPECIFICATIONS
Section 1. Program Description
1.1 Degree Name
The degree program herein shall be called BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING (BSIE).
1.2 Nature of the Field of Study
The Bachelor of Science in Industrial Engineering program is intended to prepare students for a professional Industrial Engineering career including a leading role in the design, improvement, and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment, and energy. Graduates of the program must have specialized knowledge and skills in the mathematical, physical, and social sciences together with the principles and methods of engineering analysis and design to specify, predict, and evaluate the results to be obtained from such systems.
1.3 Program Educational Objectives
Program Educational Objectives (PEOs) are broad statements describing the career and professional accomplishments the program prepares graduates to achieve within a few years of graduation. PEOs are based on the needs of the program’s constituencies and these shall be determined, articulated, and disseminated to the general public by the unit or department of the HEI offering the BSIE program. The PEOs should also be reviewed periodically for continuing improvement.
The graduates of the BSIE program are envisioned to be:
PEO 1: Individuals who will assume positions of leadership and responsibility in the application of Industrial Engineering and its allied disciplines in the public and private sectors.
PEO 2: Individuals who will continuously strive to acquire new knowledge and competencies in Industrial Engineering through continuous professional training and development.
PEO 3: Individuals who will be actively involved in contributing to the improvement of their communities, nation, and beyond.
PEO 4: Individuals who will exhibit professional attitude and ethical behavior in Industrial Engineering practice.
1.4 Specific Professions/Careers/Occupations for Graduates
Graduates of BSIE can have professions and careers as:
- Customer service engineer / manager
- Educator
- Ergonomist
- Management systems engineer / consultant
- Methods engineer
- Manufacturing engineer / manager
- Operations engineer / manager
- Operations research analyst
- Planning engineer
- Project engineer / manager
- Quality assurance engineer / manager
- Research engineer
- Systems analyst / engineer / designer
- Technopreneur
1.5 Allied Fields
The allied fields for Industrial Engineering are Mechanical Engineering, Manufacturing Engineering, Engineering Management, Statistics, Business Administration, Computer Science, and Electrical Engineering.
Section 2. Student Outcomes
The minimum standards for the BS in Industrial Engineering program are expressed in the following minimum set of institutional and BSIE program outcomes.
2.1 Institutional Outcomes
- Graduates of professional institutions must demonstrate a service orientation in one’s profession
- Graduates of colleges must participate in various types of employment, development activities, and public discourses, particularly in response to the needs of the communities one serves
- Graduates of universities must participate in the generation of new knowledge or in research and development projects
- Graduates of SUCs, in addition, must have the competencies to support “national, regional and local development plans” (RA 7722)
- A PHEI, SUC, or LUC, at its option, may adopt mission-related program outcomes that are not included in the minimum set
- Graduates of HEIs must preserve and promote the Filipino historical and cultural heritage.
2.2 BS IE Student Outcomes
The student outcomes for BS in Industrial Engineering are given in the following minimum set:
SO a. Apply knowledge of mathematics and science to solve complex engineering problems.
SO b. Conduct studies and solve problems using engineering and research methodologies.
SO c. Design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability, in accordance with standards.
SO d. Collaborate with multidisciplinary teams.
SO e. Demonstrate professional and ethical responsibility.
SO f. Communicate effectively concepts, methods, findings, and solutions across diverse audiences.
SO g. Evaluate the sustainability and impact of engineering solutions of complex problems.
SO h. Recognize and have the preparation to engage in independent and life-long learning.
SO i. Demonstrate knowledge of contemporary issues.
SO j. Utilize techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice
SO k. Practice engineering and management principles as a member and leader in a team, to manage projects and in multidisciplinary environments.
SO l. Improve integrated systems that include people, materials, information, equipment and energy.
SO m. Implement integrated systems that include people, materials, information, equipment and energy.
Section 3 Sample Performance Indicators
Performance Indicators are specific, measurable statements identifying the performance(s) required to meet the outcome; confirmable through evidence.
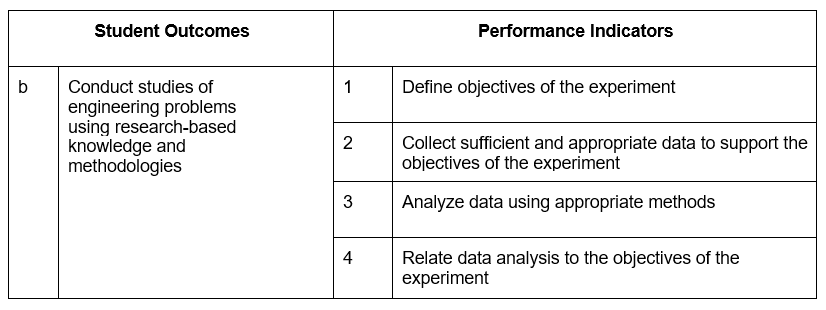
Section 4 Program Assessment and Evaluation
Program Assessment refers to one or more processes that identify, collect, and prepare data to evaluate the attainment of Program Outcomes and Program Educational Objectives.
In the case of Program Outcomes Assessment, the defined Performance Indicators shall be connected to Key Courses (usually the Demonstrating or “D” courses in the Curriculum map), and appropriate Assessment Methods (AM) may be applied. These methods may be direct or indirect depending on whether the demonstration of learning was measured by actual observation and authentic work of the student or through gathered opinions from the student or the student’s peers.
Sample Matrix Connecting Performance Indicators with Key Courses, Assessment Methods, and Target and Standard
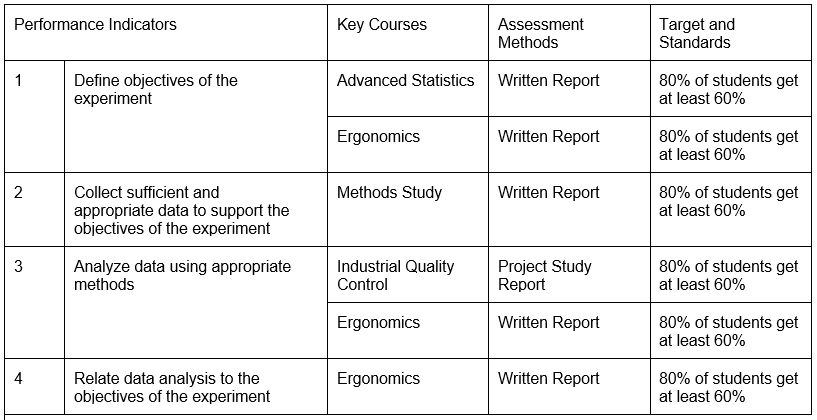
For the Assessment of Program Educational Objectives, the stakeholders of the program have to be contacted through surveys or focus group discussion to obtain feedback data on the extent of the achievement of the PEOs.
Program Evaluation pertains to one or more processes for interpreting the data and evidence accumulated from the assessment. Evaluation determines the extent at which the Program Outcomes and the Program Educational Objectives are achieved by comparing actual achievement versus set targets and standards. Evaluation results in decisions and actions regarding the continuous improvement of the program.
Other Methods of Program Assessment and Evaluation may be found in the CHED Implementation Handbook for Outcomes-Based Education (OBE) and Institutional Sustainability Assessment (ISA).

